Connecting ChatGPT to ChatGPT (2)
In the previous article, we used Python to connect to the ChatGPT API. However, as an iOS developer, I am interested in trying to directly use ChatGPT to save time and effort by helping me complete a ChatGPT integration app.
Connecting ChatGPT to ChatGPT: (1)
Starting with Generating iOS App Code Using ChatGPT
Starting with an API Request
Question:
I already have a ChatGPT API key, how can I use Swift to connect to ChatGPT?
Answer:
To use Swift to connect to ChatGPT, you can follow these steps:
Ensure you have installed the Alamofire package, which allows you to easily make HTTP requests in Swift.
Prepare an HTTP POST request with the following parameters:
URL: https://api.openai.com/v1/engines/davinci-codex/completions
Header: Authorization
Value: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
Header: Content-Type
Value: application/json
Request body: {"prompt": "YOUR_PROMPT"}
Here, YOUR_API_KEY is your ChatGPT API key, and YOUR_PROMPT is the prompt you want to send to ChatGPT.
Use the Alamofire package to send the HTTP POST request and handle the JSON formatted response:
import Alamofire
let apiURL = "https://api.openai.com/v1/engines/davinci-codex/completions"
let headers: HTTPHeaders = [
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
]
let parameters: Parameters = [
"prompt": "YOUR_PROMPT"
]
AF.request(apiURL, method: .post, parameters: parameters, encoding: JSONEncoding.default, headers: headers).responseJSON { response in
switch response.result {
case .success(let value):
// Handle the JSON formatted response
if let json = value as? [String: Any],
let choices = json["choices"] as? [[String: Any]],
let text = choices.first?["text"] as? String {
// Process the text response here
print(text)
}
case .failure(let error):
// Handle HTTP request failure here
print(error)
}
}
This way you can use Swift to connect to ChatGPT. Note that this is a simple example; you may need to make more adjustments and extensions based on your specific needs.
Next, Add a Simple Interface Including a Prompt Input, API Request Button, and Response Display
Question:
Help me generate an iOS app screen to connect to ChatGPT. The screen should have a text input box for the ChatGPT API prompt, a button below to send the API request, and a display area below that to show the response text from ChatGPT. Please use SwiftUI to create this page.
Answer:
import SwiftUI
import Alamofire
struct ContentView: View {
@State var promptText: String = ""
@State var responseText: String = ""
let apiURL = "https://api.openai.com/v1/engines/davinci-codex/completions"
let headers: HTTPHeaders = [
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
]
var body: some View {
VStack {
TextField("Enter prompt here", text: $promptText)
.padding()
.border(Color.gray)
Button(action: {
sendRequest()
}) {
Text("Send Request")
}
.padding()
Text(responseText)
.padding()
}
}
func sendRequest() {
let parameters: Parameters = [
"prompt": promptText
]
AF.request(apiURL, method: .post, parameters: parameters, encoding: JSONEncoding.default, headers: headers).responseJSON { response in
switch response.result {
case .success(let value):
if let json = value as? [String: Any],
let choices = json["choices"] as? [[String: Any]],
let text = choices.first?["text"] as? String {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
responseText = text
}
}
case .failure(let error):
print(error)
}
}
}
}
struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
ContentView()
}
}
In this code, we use @State properties to manage the states of promptText and responseText. After the user enters the prompt text, we retrieve the input from promptText. When the user presses the "Send Request" button, we send an HTTP POST request using Alamofire and process the JSON formatted response, updating the responseText. The response text is then displayed on the screen.
Note that this code is for demonstration purposes, and you may need to add more error handling and user experience in actual use.
Validating if the AI-generated Project Works
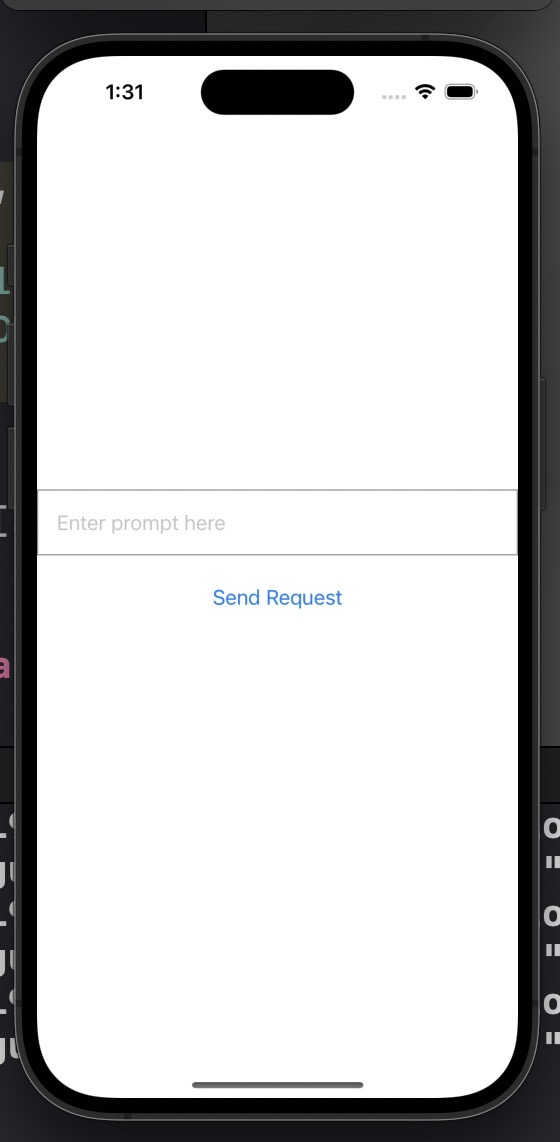
The screen looks good, so let’s see if it works. I tried entering “tell me a joke.”
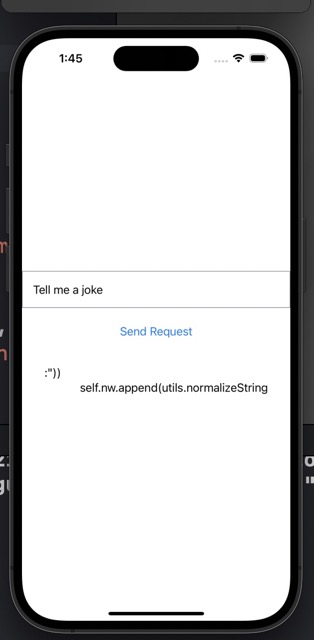
It produced a strange result, so I printed out the original response to check.
success({
choices = (
{
"finish_reason" = length;
index = 0;
logprobs = "<null>";
text = ":\"))\n self.nw.append(utils.normalizeString";
}
);
created = 1679291111;
id = "cmpl-6w2cRytpMNtkDeuiuH15Pl8qky62C";
model = "davinci-codex";
object = "text_completion";
usage = {
"completion_tokens" = 16;
"prompt_tokens" = 3;
"total_tokens" = 19;
};
})
At this point, developer intervention is needed. In its model, it used the davinci-codex model, which is not the web version that people find useful, so we swapped the endpoint.
/// Before replacement
let apiURL = "https://api.openai.com/v1/engines/davinci-codex/completions"
/// After replacement
let apiURL = "https://api.openai.com/v1/engines/text-davinci-003/completions"
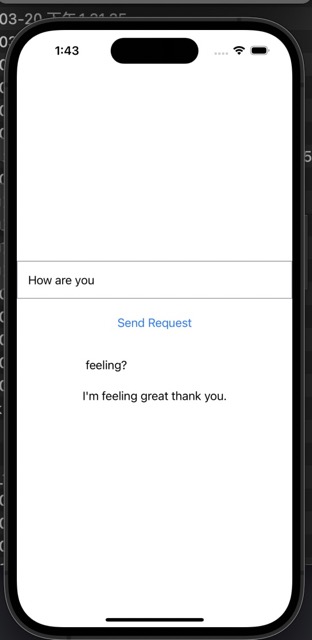
success({
choices = (
{
"finish_reason" = stop;
index = 0;
logprobs = "<null>";
text = " feeling?\n\nI'm feeling great thank you.";
}
);
created = 1679290920;
id = "cmpl-6w2ZMgsKECySpi2OFONc9HX31FJm6";
model = "text-davinci-003";
object = "text_completion";
usage = {
"completion_tokens" = 11;
"prompt_tokens" = 3;
"total_tokens" = 14;
};
})
Conclusion - At this stage, human developers still need to review ChatGPT’s code and debug
From the above examples, we can draw several conclusions:
- The code works.
- The UI meets the minimum demo standards.
- But if the prompt is not precise enough, adjustments are needed to achieve the expected human results.
